The era of “passive” supplier management is officially over. In 2026, the global supply chain has moved past the reactive firefighting of the early 2020s into a period of Connected Intelligence. Procurement leaders are no longer just looking for the lowest price; they are building resilient, transparent ecosystems where every supplier is treated as a strategic asset.
This shift has transformed Supplier Lifecycle Management (SLM) from a back-office administrative function into a front-line strategic pillar. Organizations that rely on static spreadsheets and gut-feel evaluations are being left behind by those leveraging precision tools like EvaluationsHub.
The Architecture of Modern Supplier Lifecycle Management
Today, SLM is organized as a continuous, circular process rather than a linear checklist. It’s about managing the “health” of the relationship from the first handshake to the final offboarding.
1. Strategic Identification & Qualification
In 2026, finding a supplier isn’t just about capability; it’s about alignment. Procurement teams use AI-driven sourcing to identify partners who not only meet technical specs but also align with the company’s ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and digital maturity.
-
The 2026 Standard: Qualification now includes a “Digital Readiness” score, ensuring the supplier can integrate into your data ecosystem.
2. Frictionless Onboarding
Old-school onboarding took weeks of manual document chasing. Modern SLM uses automated workflows to collect certifications, tax data, and security audits.
-
The Evolution: Self-service portals allow suppliers to upload their own data, which is then verified by automated “truth-checking” bots, reducing the “time-to-productivity” for new vendors by up to 60%.
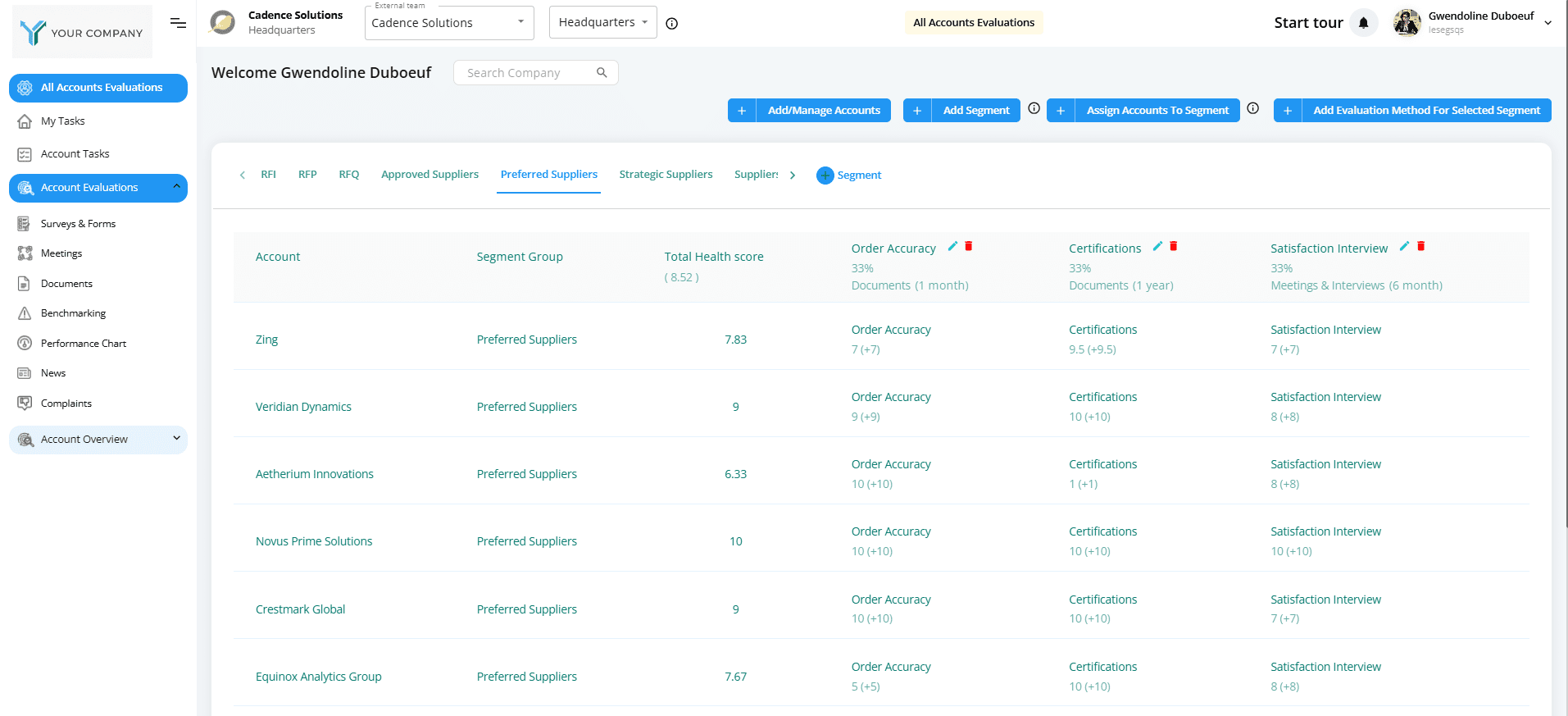
3. Precision Performance Management (The “EvaluationsHub” Layer)
This is where the most significant change has occurred. Instead of an annual “How are they doing?” meeting, companies now use 360-degree, event-driven scorecards.
-
Dynamic Feedback: Tools like EvaluationsHub trigger evaluations based on real events—like a late delivery in SAP or a quality defect logged in the warehouse.
-
Multisided Input: It’s no longer just the buyer’s opinion. Input is gathered from the warehouse, the finance team, and even the supplier themselves to create a truly objective performance record.
4. Continuous Risk and ESG Vigilance
Risk management is no longer a periodic audit. It is continuous. 2026 SLM systems monitor geopolitical shifts, financial fluctuations, and carbon footprint data in real-time. If a supplier’s risk profile changes, the system doesn’t just send an alert—it triggers a pre-defined mitigation workflow.
5. Strategic Development & Offboarding
The final stage isn’t just “ending” a contract. It’s about Supplier Development. If a high-value supplier is underperforming in one area, modern SLM uses data to build a Corrective Action Plan (CAPA). If the relationship must end, “clean offboarding” ensures that all data is purged and intellectual property is secured.
Why Legacy Systems are Failing the 2026 Procurement Leader
Many enterprises still try to manage SLM within their primary ERP. While ERPs are great for transactions, they are notoriously “stone-age” when it comes to human collaboration and qualitative data.
-
The Data Silo Trap: Quantitative data (price, quantity) lives in the ERP. Qualitative data (reliability, innovation, communication) lives in emails and Excel.
-
The “Black Box” Problem: Suppliers often have no idea how they are being measured until it’s too late.
-
The Manual Burden: Chasing internal stakeholders for feedback is the most hated task in procurement.
How EvaluationsHub Closes the Loop
This is where a specialized tool like EvaluationsHub becomes the “central nervous system” of your supplier strategy. It doesn’t replace your ERP; it makes your ERP smarter by adding the “human and event” layer that is usually missing.
1. The Power of “Event-Driven” Scorecards
EvaluationsHub doesn’t wait for you to remember to evaluate a supplier. It plugs into your existing systems (SAP, Salesforce, etc.) and waits for a trigger.
Example: A “Goods Receipt” is posted with a quality defect code. EvaluationsHub immediately sends a micro-survey to the Quality Manager: “You just received a defective batch from Supplier X. Was the issue resolved quickly?” This captures real-time sentiment that an annual review would forget.
2. 360-Degree Feedback (Not just Top-Down)
In 2026, the most successful companies treat suppliers as partners. EvaluationsHub facilitates this by allowing for two-way evaluations. Suppliers can rate the buyer on “payment timeliness” or “clarity of specifications.” This transparency builds the trust required for long-term innovation.
3. Actionable Insights vs. Static Data
Most tools tell you what happened. EvaluationsHub tells you what to do. By aggregating scores across regions and departments, it identifies systemic issues.
-
If a supplier is performing well in Europe but failing in Asia, the tool flags the discrepancy, allowing for targeted development rather than a broad contract termination.
The 2026 Edge: Agentic AI in SLM
As we move deeper into 2026, Agentic AI has become the secret weapon of the pro procurement team. Unlike standard AI that just summarizes text, AI Agents in tools like EvaluationsHub actually act.
-
The “Nudge” Agent: Automatically follows up with internal stakeholders who haven’t completed their evaluations, adjusting the tone based on the person’s historical responsiveness.
-
The “Contract-Alignment” Agent: Compares current performance data against the SLAs written in the contract. If a supplier falls below a threshold, the agent drafts the “Notice of Non-Performance” for the human buyer to review.
-
The “Pattern Recognition” Agent: Sees that a supplier’s delivery times are creeping up by 2% every month—a trend a human would miss—and flags it as a potential sign of financial instability.
The Business Impact: Beyond the Bottom Line
Organizing SLM through a structured, tool-assisted approach isn’t just about saving money. It’s about Total Value.
| Metric | Legacy Method (Excel/Email) | Modern Method (EvaluationsHub) |
| Evaluation Completion Rate | 30–40% | 95%+ |
| Time Spent on Admin | 15 hours/month per buyer | 2 hours/month per buyer |
| Data Accuracy | Subjective / Biased | Objective / Evidence-linked |
| Supplier Relationship | Transactional / Adversarial | Strategic / Collaborative |
Conclusion: Building the “Supplier-of-Choice” Status
In 2026, the market is tight. The best suppliers have their pick of customers. If you are a “difficult” customer—one with messy data, slow feedback, and unclear expectations—the best suppliers will prioritize your competitors.
By organizing your Supplier Lifecycle Management with a professional framework and empowering it with EvaluationsHub, you aren’t just managing vendors; you are becoming a Customer of Choice. You gain the transparency to fix issues before they become crises and the data to reward excellence where it matters most.
The question for procurement leaders today isn’t if they should modernize their SLM, but how fast they can do it before their competitors leverage these tools to snap up the best partners in the market.